When Your Child Has an Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
When Your Child Has an Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
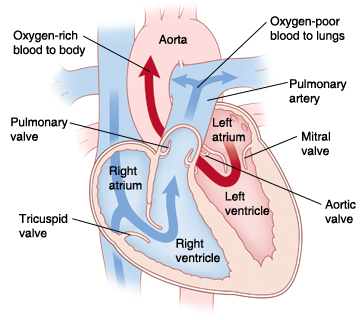
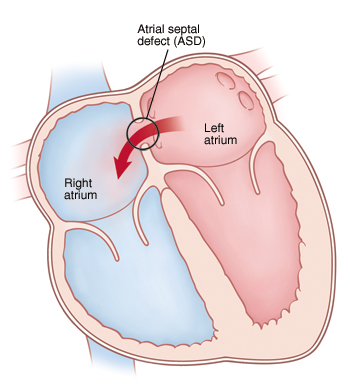
The heart has 4 chambers. An atrial septal defect (ASD) is a hole in the dividing wall (atrial septum) between the 2 upper chambers (atria) of the heart. There are 4 types of atrial septal defects:
Sinus venosus defect occurs in the superior or inferior parts of the atrial septum.
Secundum defect occurs in the middle part of the atrial septum.
Primum defect occurs in the part of the atrial septum, next to the heart valves.
Coronary sinus defect occurs when part or the entire common wall between the coronary sinus (which normally drains into the right atrium) and left atrium is absent.
An ASD can lead to certain heart problems over time. But it can often be treated.
Diagram of normal heart showing the 4 heart chambers and the atrial septum. |
An ASD lets more blood than normal circulate through the right side of the heart and the lungs. |
What causes an atrial septal defect?
An ASD is a congenital heart defect. This means it’s a problem with the heart’s structure that your child was born with. It can be the only defect, or it can be part of a more complex set of defects. The exact cause is unknown, but most cases seem to occur by chance. Having a family history of heart defects can be a risk factor.
Why is an atrial septal defect a problem?
Blood normally flows from chamber to chamber in 1 direction through the left and right sides of the heart. With an ASD, blood typically flows through the defect from the left atrium to the right atrium. This is called a left-to-right shunt. It causes more blood than normal to circulate through the right side of the heart. As a result, extra blood has to be pumped by the right side of the heart to the lungs. Over time, too much blood flow to the lungs can increase the pressure in the pulmonary arteries (blood vessels leading from the heart to the lungs). Left untreated, the pulmonary arteries can become damaged. Irreversible lung problems can eventually occur in adulthood.
What are the symptoms of an atrial septal defect?
Most children with an ASD appear to be in normal health and have no symptoms. If symptoms are present, they can include:
Tiring easily during exercise
Difficult and rapid breathing
Frequent pneumonias
Slow growth
Migraine headaches in older children
Stroke from blood clot
Arrhythmias or abnormal heartbeats increasing with age if the ASD foes unrepaired
How is an atrial septal defect diagnosed?
During a physical exam, the doctor checks for signs of a heart problem such as a heart murmur. This is an extra noise caused when blood doesn’t flow smoothly through the heart. If your child's doctor suspects a heart problem, your child will be referred to a pediatric cardiologist. This is a doctor who diagnoses and treats heart problems in children. To check for an ASD, the following tests may be done:
Chest X-ray. X-rays are used to take a picture of the heart and lungs.
Electrocardiogram (ECG). The electrical activity of the heart is recorded.
Echocardiogram (echo). Sound waves (ultrasound) are used to create a picture of the heart and look for structural defects.
How is an atrial septal defect treated?
Certain ASDs (such as smaller secundum defects) may close on their own in the first few years of life. So the cardiologist may check your child’s heart regularly and wait to see if an ASD closes or becomes smaller.
If an ASD is moderate or large or doesn’t close on its own by the time your child is school age, your child's cardiologist may advise repair. This can be done wither using cardiac catheterization or open heart surgery. The cardiologist will evaluate your child’s condition and discuss treatment options with you.
What are the long-term concerns?
An ASD that’s left untreated can lead to further health problems later in life. These can include high blood pressure in the lungs, lung disease, and a higher risk of stroke as an adult.
After treatment, most children with an ASD can be as active as other children. Talk with your cardiologist about any activity restrictions.
Regular follow-up visits with the cardiologist are needed. The frequency of these visits will likely decrease or cease as your child grows older.
Your child may need to take antibiotics before having any surgery or dental work for 6 months after the ASD repair. This is to prevent infection of the inside lining of the heart and valves. This infection is called infective endocarditis. You should discuss this with your child's cardiologist.
Updated:
August 16, 2018
Sources:
Classification of atrial septal defects, and clinical features and diagnosis of isolated ASDs in children, Up To Date
Reviewed By:
Ayden, Scott, MD,Bass, Pat F. III, MD, MPH,Image reviewed by StayWell medical illustration team.