What Is Prostate Cancer?
What Is Prostate Cancer?
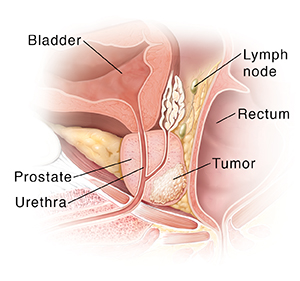
Understanding the prostate
The prostate is a gland in men about the size and shape of a walnut. It surrounds the upper part of the urethra. This is the tube that carries urine from the bladder. The prostate makes some of the fluid that’s part of semen. During orgasm, semen leaves the body through the urethra.
When prostate cancer forms
As a man ages, the cells of his prostate may change to form tumors or other growths. The types of growths include:
Noncancerous growths. As a man ages, the prostate may grow larger. This is called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). With BPH, extra prostate tissue often squeezes the urethra, causing symptoms such as trouble urinating. But BPH is not cancer and does not lead to cancer.
Atypical cells. Sometimes prostate cells don’t look like normal (typical) prostate cells. One type of abnormal growth is called prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia or PIN. Although PIN cells are not cancer cells, they may be a sign that cancer is likely to form.
Cancer. When abnormal prostate cells grow out of control and start to invade other tissues, they are called cancer cells. These cells may or may not lead to symptoms. Some tumors can be felt during a physical exam, and some can’t. Prostate cancer may grow into nearby organs or spread to nearby lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small organs around the body that are part of the immune system. In some cases, the cancer spreads to bones or organs in distant parts of the body. This is called metastasis.
Diagnosing prostate cancer
Prostate cancer may not cause symptoms at first. Urinary problems are often not a sign of cancer, but of another condition, such as BPH. To find out if you have prostate cancer, your healthcare provider must examine you and order tests. The tests help confirm a diagnosis of cancer. They also help give more information about a cancerous tumor. Tests might include:
Prostate specific antigen (PSA) testing. PSA is a chemical made by prostate tissue. The amount of PSA in the blood (PSA level) is tested to check a man’s risk for prostate cancer. In general, a high or rising PSA level may mean an increased cancer risk. A PSA test by itself cannot show if a man has prostate cancer. PSA testing is also used to check the success of cancer treatments.
Core needle biopsy. This test is done to determine if a man has prostate cancer. A hollow needle is used to take small pieces of tissue from the prostate. This helps give more information about the cells. Before the test, pain medicine may be given to prevent pain. During the test, a small probe is inserted into the rectum. The probe sends an image of the prostate to a video monitor. With this image as a guide, the healthcare provider uses a thin, hollow needle to remove tiny tissue samples from the prostate. These are sent to a lab where they are looked at for cancer cells.
Updated:
May 19, 2017
Reviewed By:
Gersten, Todd, MD