Postural Drainage
Postural Drainage
Postural drainage is a way to change your body position to help your lungs drain. If you have a chronic lung problem with mucus, or you have increased mucus from an infection, lying with your chest lower than your belly (abdomen) can help loosen and drain extra mucus from your lungs. The following guidelines will help you know what to do.
Back |
Side |
Stomach |
General guidelines
Find positions that are comfortable for you. You can lie on a bed or on the floor, using pillows. Try some of the positions that are described below.
Stay in each position for at least 5 minutes.
When you feel the urge to cough, sit up and do controlled coughing.
Make sure to do postural drainage on an empty stomach. Also do it 30 minutes after using a bronchodilator or inhaler.
Check with your doctor before trying this therapy.
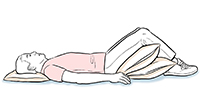
On your back
Try this position to drain the front of your lungs.
Lie on a slanted surface with your chest lower than your hips.
Place a small pillow under your head. Put 2 pillows under your bent knees.
Rest your arms at your sides and breathe in through your nose and out through your mouth. Remember: Always breathe out for longer than you breathe in. This allows your lungs to empty as much as possible.
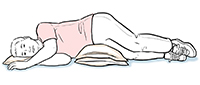
On each side
Try this position to drain the sides of your lungs.
Place a small pillow under your head and 2 or 3 pillows under your hips.
Lie on one side with your chest lower than your hips.
Breathe in through your nose. Breathe out through your mouth.
After 5 to10 minutes, switch to the other side.
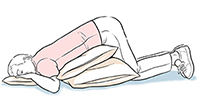
On your stomach
Try this position to drain the back of your lungs.
Put 2 or 3 pillows under your stomach.
Drape your body over the pillows so that your chest is lower than your hips.
Rest your arms by your head.
Breathe in through your nose. Breathe out through your mouth.
Follow-up care
Make a follow-up appointment as directed by our staff.
When to call your healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following:
Wheezing or constant coughing
Increased mucus
Yellow, green, brown, bloody, or smelly mucus
Fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your healthcare provider
Tightness in your chest that does not go away with rest or medicine or sudden sharp pain in the chest area
Fast or irregular heartbeat
Swollen ankles
Pain
Call 911
Shortness of breath may be a sign of a serious health problem. Call 911 if you have shortness of breath that gets worse or have trouble breathing, especially with any of the symptoms below:
Confusion or difficulty staying awake
Loss of consciousness or fainting
Chest pain or tightness
Difficulty breathing or wheezing
Bluish skin
Coughing up blood
Severe pain
Updated:
April 19, 2018
Sources:
Cystic Fibrosis Pulmonary Guidelines: Airway Clearance Therapies. Flume, PA. Respiratory Care. 2009;54(4):s522-37.
Reviewed By:
Demuro, Jonas, MD,Fetterman, Anne, RN, BSN,Image reviewed by StayWell art team.