Discharge Instructions: Giving an Intramuscular (IM) Injection in the Hip
Discharge Instructions: Giving an Intramuscular (IM) Injection in the Hip
You were shown how to do an IM injection in the hospital. If you did not get an instruction sheet covering those general steps, ask for one. This sheet reminds you or your caregiver how to give an IM injection in the hip. Another person must help you with this injection.
Name of your medication: _______________________________.
Amount per injection: _________________________________.
Times per day: ______________________________________.
Step 1. Getting ready
Gather your supplies.
Wash your hands well. The person who is helping you must also wash his or her hands well.
Prepare your medicine as you were shown by your healthcare provider.
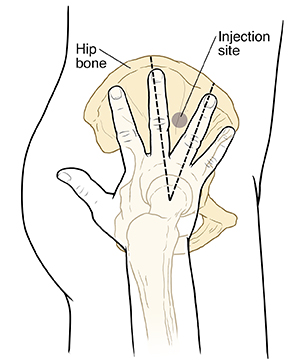
Step 2. Finding an injection site
The person who is helping you can find an injection site on your hip by doing the following:
The other person will find the place where your thighbone meets your hip. This is a bony, ball-like area. The other person will place the palm of his or her hand over this bony area.
The other person’s fingers should point toward the ceiling. Then he or she will make a V with the ring finger and middle finger.
The bottom point of the V is where the other person’s ring finger and middle finger meet.
The injection site will be between the knuckles on the other person’s ring finger and middle finger. This is where the needle will be inserted.
The other person will prepare the injection site as you were shown by your healthcare provider. (See the general instruction sheet on giving yourself an IM injection. If you did not get this sheet, ask for one.)
Step 3. Injecting the medicine
The other person will stretch your skin tight.
The other person will hold the syringe like a pencil. Then he or she will insert the needle straight into your skin.
You should have no more than 4 mL of medicine in this site. If the prescribed dose is more than 4 mL, choose a different site to inject the medicine.
Step 4. Removing the needle
The other person will remove the needle and syringe outward, away from your body.
He or she will let go of your skin.
Step 5. After the injection
The other person will put the needle and syringe in a special container (sharps container).
Dispose of the other materials as you were shown by your healthcare provider.
Wash your hands well. The person who is helping you must also wash his or her hands well.
Medicine that comes in a container for a single dose should be used only 1 time. If you use it a second time, it may have germs that can cause infections. These infections usually affect the skin and soft tissues. But some infections can affect the brain, spinal cord, or heart. Sharing another person's used needles or medicines can cause other infections such as hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your healthcare provider, or as advised.
When to seek medical care
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following:
Needle that breaks off at the injection site
Problems that keep you from getting the injection
Bleeding or severe pain at the injection site that won’t stop
Medication injected into the wrong area
Rash or swelling at the injection site
Shortness of breath
Fever above 100.4°F (38.0°C)
Updated:
April 24, 2017
Sources:
IM Injection, Lippincott's Nursing Procedures. StatRef.
Reviewed By:
Image reviewed by StayWell medical illustration team.,Perez, Eric, MD,Ziegler, Olivia, MS, PA