Stress Echocardiography (Echo)
Stress Echocardiography (Echo)
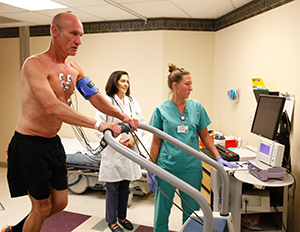
Before your test
When you schedule your test, mention all medicines you take. Ask if it’s OK to take them before your test. Certain medicines can affect blood flow to the heart and the heart rate and affect the test results. You may be asked to wait until after the test is complete before you take your usual doses of these types of medicines.
Discuss any questions or concerns you have with your healthcare provider.
Allow extra time to check in. Bring your insurance cards, identification, and any co-payments that are required for the test.
For 4 hours before the test, don’t eat or drink. Don't drink any caffeine for 12 hours before the test, or as directed by your healthcare provider. If you use tobacco, you may also be asked not to use it the day of the test. This includes electronic cigarettes, chew, and nicotine gum. Stimulating the heart with these substances can affect your test results.
Wear flat, comfortable walking shoes.
Wear a top you can take off easily. You may be asked to remove your clothing from the waist up. If you are a woman, you will be given a hospital gown to wear.
An intravenous catheter may be inserted into a vein in your arm or hand. Contrast or bubbles will be injected during the study.
During your test
Echo uses a small device that makes sound waves (transducer). It sends images of your heart to a video monitor. The images are recorded:
A special gel is put on your chest. The transducer is moved over the gel. This records your heart at rest. If you are overweight, the technician may have to apply more pressure to get the best quality images. This can be uncomfortable over body areas. Tell your technician if you are uncomfortable.
Your blood pressure is taken. An electrocardiogram (ECG) is also done. This test involves small pads called electrodes. They are placed on your chest. The ECG reads the pattern of your heartbeat.
Next, you’re asked to walk on a treadmill or pedal a stationary bike. You’ll do this until your heart beats rapidly. Note: If you are not able to exercise, you’ll be given a medicine to get your heart working harder, this medicine can make you feel short of breath.
You stop exercising. Right away, the transducer is used to take a second set of video images of your heart. Your healthcare provider compares these images to the first ones taken.
The technician may use IV contrast to improve the image quality or agitated saline may be used to follow blood flow through the chambers of the heart.
During the test, be sure to tell the healthcare provider if you feel any chest, arm, or jaw discomfort. Also mention if you have severe shortness of breath, feel very tired, or feel dizzy. The test may be stopped if you have severe or persistent symptoms with exercise or there is any change in your vital signs or heart rhythm.
After the test
You can go back to your normal daily routine. Be sure to keep your follow-up appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss test results.
Your next appointment is: _______________________
Updated:
December 16, 2017
Sources:
Exercise ECG testing: Performing the test and interpreting the ECG results. UpToDate.
Reviewed By:
Gandelman, Glenn, MD, MPH,Image reviewed by StayWell art team.,Snyder, Mandy, APRN