Diagnosing a Parathyroid Problem
Diagnosing a Parathyroid Problem
Your healthcare provider thinks you may have a parathyroid problem. He or she will ask you about your medical history and give you a physical exam. You may need to have blood tests. You may also need to have other tests, such as an imaging scan. Based on the results, your healthcare provider will work with you on a treatment plan.
|
Medical history
Your healthcare provider will ask about your medical history. Tell him or her about:
Symptoms you have, even if they seem minor
Health conditions you have, or had in the past
What foods you eat
The medicines and supplements you use
Physical exam
During a physical exam, your healthcare provider will feel your neck. He or she may also check other parts of your body to look for other causes of your symptoms.
Blood and urine tests
Certain tests are done to diagnose primary hyperparathyroidism and to rule out other causes of problems. The risk of related health problems, such as kidney and bone disease, is also evaluated. Tests may include:
Blood tests. Samples of blood are drawn from a vein. These are checked for high levels of calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH). The levels of vitamin D, magnesium, alkaline phosphatase, and phosphorus may also be checked.
Urine tests. Samples of urine are taken over a 24-hour period. These are checked for high levels of calcium and signs of kidney problems. Urine testing could find a type of high calcium which runs in families which would not need surgery.
Imaging tests
Imaging tests can help show if parathyroid glands are enlarged, and can check your bones for signs of calcium problems. You may have one of the below:
Bone density study. Scans of the hip, lower back, or forearm are taken. This test measures the amount of calcium in the bones to check bone health.
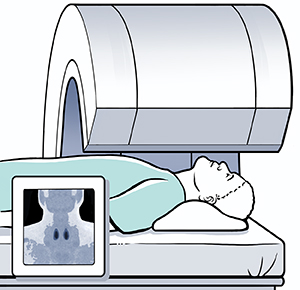
Sestamibi scan. This is used to show enlarged parathyroid glands. The test can take up to 3-4 hours. During the test, a safe radioactive fluid is injected into the veins. This fluid helps make enlarged parathyroid glands show up clearly when a special camera is used.
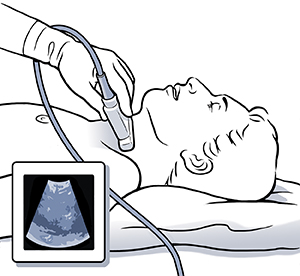
Ultrasound. This test can also be used to show enlarged parathyroid glands. During this quick test, harmless sound waves are used to form pictures of the parathyroid glands. The pictures are then viewed on a computer screen.
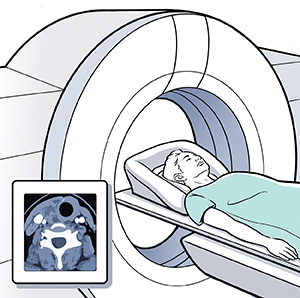
Computed tomography (CT) scan. This test uses a series of many X-rays and a computer to form detailed images.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This testuses magnets and radio waves to form images. This test is used less often, but they can also be used to show enlarged parathyroid glands.
Updated:
March 21, 2017
Sources:
Up To Date. Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis of Primary Hyperparathyroidism
Reviewed By:
Freeborn, Donna, PhD, CNM, FNP,Hurd, Robert, MD