Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography (Echo)
Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography (Echo)
Before your test
Tell your healthcare provider what medicines you take, and ask if you should take them before the test. Don’t smoke, drink alcohol, or have any caffeine for 12 hours before the test, or as directed by your healthcare provider. Don't eat for at least 4 hours before the test. Make sure to wear a two-piece outfit. You may need to undress from the waist up and put on a short hospital gown. Allow an extra hour for checking in and getting ready for the test.
During your test
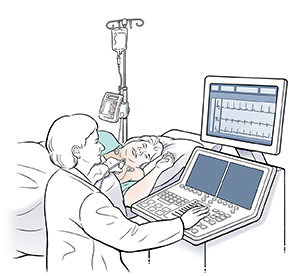
Your healthcare provider places small pads (electrodes) on your chest to record the electrical activity of your heart.
He or she starts an intravenous (IV) line in your arm.
A painless device (transducer) coated with cool gel is moved firmly over your chest. This device creates ultrasonic, inaudible sound waves that make images of your heart on a screen.
Your healthcare provider slowly gives you dobutamine through the IV, in small doses about every 3 minutes. It is normal to feel your heart pound for a few minutes, while the medicine is being given.
Your healthcare provider will take echo images before the infusion of the drug, during the infusion, and after your pulse returns to normal. Your healthcare provider may give you a second medicine to slow your heartbeat to a normal level.
Your healthcare provider will monitor your heart and blood pressure during and after the test.
After your test
When the test is over, you may return to your normal routine. Ask your healthcare provider about taking any medicine that you were told to skip before the test. Your healthcare provider will discuss your test results with you. The test results help your provider plan your treatment and any other tests you may need.
Report any symptoms
Be sure to tell your healthcare provider if you feel any of the following during the test:
Chest, arm, or jaw discomfort
Irregular heartbeat
Feeling flushed
Palpitations
Shortness of breath
Nausea
Headache
Numbness
Lightheadedness or like you might faint
Updated:
June 15, 2018
Sources:
American Society of Echocardiography recommendations for performance, interpretation, and application of stress echocardiography. Pellikka, PA. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography. 2007;20(9):1021-41., Bach, D., Dobutamine Stress Echocardiogram, Circulation (1999)95; 8-10, Impact of medications and methylxanthines on stress testing, Up To Date, Overview of stress echocardiography, Up To Date, Pellikka, PA, Recommendations for performance interpretation and application of stress echocardiography. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography (2007); 30(9); 1021-1041
Reviewed By:
Gandelman, Glenn, MD, MPH,Image reviewed by StayWell medical illustration team.,Snyder, Mandy, APRN