Refractive Surgery: LASIK
Refractive Surgery: LASIK
LASIK (pronounced LAY-sik) stands for laser in-situ keratomileusis. It's a technique for reshaping corneal tissue to help you see better without glasses or corrective lenses. This procedure uses an excimer laser, which produces a concentrated beam of cool ultraviolet (UV) light. Each pulse of the laser can remove a tiny part of corneal tissue. LASIK can be used to correct the following conditions:
Farsightedness (hyperopia)
Nearsightedness (myopia)
Blurred vision caused by an abnormally shaped cornea (astigmatism)
What to expect during the procedure
Before treatment, you may be given medicine to help you relax.
Eye drops numb your eyes. A device is used to keep your eyes open.
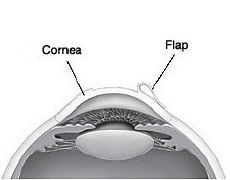
You may feel light pressure, but no pain, as your surgeon makes the flap in the top layer of your cornea (epithelium). The flap is folded back, but stays attached to the cornea.
Your surgeon uses a computer-guided excimer laser to reshape the cornea. Laser treatment lasts for 10 to 90 seconds.
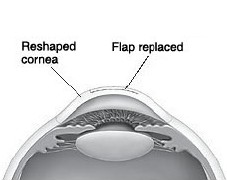
The flap is put back into place. The corneal tissue sticks to itself while it heals.
After treatment, your vision will start to get better right away. It should become stable in 1 to 3 months.
Pros of LASIK
Little or no pain after surgery
Fast recovery
Very accurate, even for severe refractive problems
Serious haze after surgery unlikely
Structure of cornea stays intact
Cons of LASIK
Risk of flap complications, infection, or inflammation
Risk of blurred or distorted vision
Possible short-term (temporary) or long-lasting (permanent) dry eye
Risk of night vision problems, such as halos, glare, or starbursts
Possible undercorrection or overcorrection
Possible loss of your best corrected vision
Updated:
March 21, 2017
Reviewed By:
Bogus, William J., OD, FAAO,Griggs, Paul B., MD,Image reviewed by StayWell medical illustration team.