Anatomy of the Ear
Anatomy of the Ear
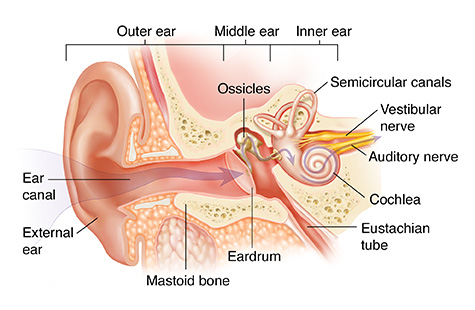
The ear is a complex and delicate organ. It collects sound waves so you can hear the world around you. The ear also has a second function—it helps you keep your balance. Your ear can be divided into 3 parts. The outer ear and middle ear help collect and amplify sound. The inner ear converts sound waves to messages that are sent to the brain. The inner ear also senses the movement and position of your head and body so you can maintain your balance and see clearly, even when you change positions.
The mastoid bone surrounds the middle ear. The external ear collects sound waves. The ear canal carries sound waves to the eardrum. The eardrum vibrates from sound waves, setting the middle ear bones in motion. The middle ear bones (ossicles) vibrate, transmitting sound waves to the inner ear. When the ear is healthy, air pressure remains balanced in the middle ear. The eustachian tube helps control air pressure in the middle ear. The semicircular canals help maintain balance. The vestibular nerve carries balance signals to the brain. The auditory nerve carries sound signals to the brain. The cochlea picks up sound waves and makes nerve signals.
Updated:
June 26, 2017
Reviewed By:
Fraser, Marianne, MSN, RN,Images reviewed by StayWell medical illustration team.,Kacker, Ashutosh, MD