Diabetes and Your Child: The A1c Test
Diabetes and Your Child: The Hemoglobin A1C Test
What is the A1C test?
The A1C is a simple blood test. It measures your child’s average blood sugar level over a period of 2 to 3 months. This is helpful because it tells how well your child's blood sugar is controlled. The better your child's blood sugar is controlled, the less likely he will develop complications of diabetes. Other tests your child may have include fasting blood glucose, glucose tolerance test, or random blood glucose test only show blood sugar levels at a specific time. These tests don't give much information about control.
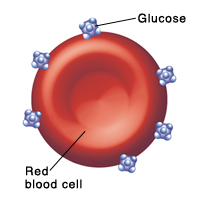
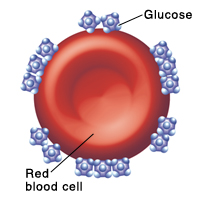
A1C works by measuring the amount of glucose that sticks to a protein called hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is found in red blood cells. The more glucose stuck to the red blood cells, the higher your child’s average blood sugar has been.
An A1C result is given as a percentage. Most people without diabetes have an A1C level of 5.7% or lower.
Your child’s target A1C number
Your child’s healthcare provider will tell you what your child’s target A1C number should be. It will depend on his or her age, overall health, and other factors. Your child will likely need an A1C test about once every 3 months. In general, the A1C goal for children and adolescents is less than 7.5%.
Resources
For more information about diabetes, visit these websites:
American Diabetes Association www.diabetes.org
Children with Diabetes www.childrenwithdiabetes.org
Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation www.jdrf.org
American Association of Diabetes Educators www.aadenet.org
American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists www.aace.com
National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse www.diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
Updated:
October 09, 2017
Sources:
Management of type 1 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. UpToDate, Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes, 2017, American Diabetes Association
Reviewed By:
Adler, Liora C., MD,Image reviewed by StayWell medical illustration team.,Sather, Rita, RN,Turley, Raymond Kent, BSN, MSN, RN