Staff Ed: Droplet Transmission
Transmission-Based Precautions: Droplet
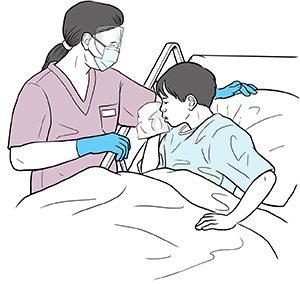
When to use droplet precautions
Some germs are carried in moist droplets. These drops travel a short distance (about 3 feet) when an infected person coughs, talks, or sneezes. The drops also contaminate objects and surfaces they fall on. Use droplet precautions with patients known or suspected to have certain infections as outlined by your facility, including:
Pertussis (whooping cough)
Neisseria meningitidis
Haemophilus influenza type B
Influenza
Scarlet fever
Mumps
Rubella (German measles)
How to use droplet precautions
The patient should be placed in a private room with a private bathroom. If this can’t be done, check with your facility’s infection control department. Also:
Wear a mask when within 3 feet of the patient. Or you may wear a mask at all times when in the patient’s room. Follow your facility’s guidelines.
Keep other patients at least 3 feet away from the infected patient.
Have family members and other visitors wear masks and other appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
Transport the patient only when you must. Have the patient wear a surgical mask. Alert the receiving department.
Preventing contamination
Remove your gloves and other PPE before leaving the room. Wash your hands well before leaving.
The infected patient should have his or her own patient care equipment (including stethoscope, blood pressure cuff, thermometer, and commode). If an item must be shared, clean it with disinfectant between patients.
If you touch an object in the room with your gloves, change them before providing care to any patient.
Don't touch your mouth, nose, or eyes during patient care.
Updated:
June 28, 2018
Sources:
Types of precautions for infection control, Up To Date
Reviewed By:
Freeborn, Donna, PhD, CNM, FNP,Hurd, Robert, MD,Image reviewed by StayWell medical illustration team.