Adrenal Cancer: Frequently Asked Questions
Adrenal Cancer: Frequently Asked Questions
What is adrenal cancer?
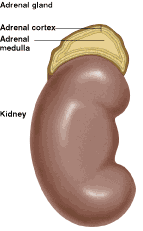
Adrenal cancer is a rare cancer that begins in the adrenal glands. The adrenal glands are a pair of small organs. There is one above each kidney.
The adrenal glands produce hormones known as glucocorticoid steroids, which help control the metabolism of protein, fat, and carbohydrates. They also produce mineralocorticoids, which regulate the amount of sodium and potassium in body fluids. The glands produce small amounts of the sex hormones estrogen and androgen. The adrenal glands also secrete the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine, which help regulate the part of the nervous system that controls the heart muscles and the digestive and respiratory systems. The adrenal cortex is the outside layer of the adrenal glands. The inside layer is called the adrenal medulla.
What are the types of adrenal cancer?
These are the two types of adrenal cancer:
Cancer of the adrenal cortex. This cancer affects cells in the outer layer of the adrenal gland. It is also called adrenocortical carcinoma.
Pheochromocytoma. This is a cancer of the adrenal medulla, the inside of the adrenal glands. Pheochromocytoma can also start in other parts of the body, but it most commonly occurs in the adrenal gland.
What are the symptoms of adrenal cancer?
Patients with adrenal cancer may have any or all of the following symptoms:
Pain in the abdomen or back
A lump or feeling of fullness in the belly (abdomen)
Unexplained weight loss or weight gain
Weakness
Hirsutism (increased hairiness occurring mostly in women) or virilism (causes woman to develop masculine features)
High blood pressure that is hard to control
New diabetes (high blood sugar) that is hard to control
Cancer of the adrenal cortex can cause high blood pressure, weakening of the bones, and diabetes. People with this type of adrenal cancer may experience deepening of the voice, hair growth on the face, and swelling of the sex organs or breasts. These symptoms may happen if male or female hormones are affected.
People with pheochromocytomas may develop high blood pressure, which can cause chest pain, sweating, headaches, pounding of the heart, and anxiety.
It is important to remember that these symptoms can be caused by many other medical problems. If a person has any of these symptoms, he or she should see a doctor as soon as possible.
How is adrenal cancer treated?
Treatment for adrenal cancer is either local or systemic. Local treatments remove, destroy, or control the cancer cells in one certain area. Surgery and radiation are local treatments. Systemic treatments destroy or control cancer cells throughout the entire body. Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment. A patient may have just one treatment or a combination of treatments.
Surgery. The goal of surgery is to remove the tumor along with the adrenal gland. Sometimes the nearby lymph nodes are also removed.
Radiation therapy. The goal of radiation is to kill cancer cells by using high energy X-rays. This treatment is used to treat any remaining cancer cells after surgery or areas of cancer spread (metastasis).
Chemotherapy. The goal of chemotherapy is to shrink the adrenal cancer, by stopping the growth of cancer cells, while also reducing the chance that the cancer will spread to other parts of the body.
Doctors are always looking for new ways to treat adrenal cancer. These new methods are tested in clinical trials. Before beginning treatment, a person should ask a doctor if there are any clinical trials available that he or she should consider.
What are clinical trials?
Clinical trials are studies of new kinds of cancer treatments. Doctors conduct clinical trials to learn about how well new treatments work and what their side effects are. If they look promising, they are then compared to the current treatment to see if they work better or have fewer side effects. People who participate in these studies may benefit from access to new treatments before the FDA approves them. Participants also help further our understanding of cancer and help future cancer patients.
Should everyone get a second opinion?
Many people with cancer get a second opinion from another doctor. There are many reasons to get a second opinion, including if the person is not comfortable with the treatment decision, if the type of cancer is rare, if there are different ways to treat the cancer, or if the person is not able to see a cancer expert.
How can someone get a second opinion?
There are many ways to get a second opinion:
The person's primary doctor may be able to recommend a cancer specialist, such as a surgeon, medical oncologist, or radiation oncologist. Sometimes these doctors work together at cancer centers or programs.
The Cancer Information Service (800-4-CANCER) informs callers about treatment facilities, including cancer centers and other programs supported by the National Cancer Institute.
Patients can get names of doctors from their local medical society, a nearby hospital, a medical school, or local cancer advocacy groups, as well as from other people who have had that type of cancer.
Updated:
March 23, 2017
Reviewed By:
Gersten, Todd, MD,Stump-Sutliff, Kim, RN, MSN, AOCNS