Urethritis in Women
Urethritis in Women
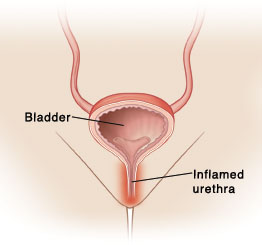
Urethritis occurs when the urethra is inflamed (red and swollen). This is the tube that passes urine from the bladder to outside the body. The urethra can become swollen and cause burning pain when you urinate. You may also have pain with sex. It can cause pain in the abdomen or pelvis. A urethral or vaginal discharge may also occur.
What causes urethritis?
Urethritis can be caused by a bacterial or viral infection. Such an infection can lead to conditions such as a urinary tract infection (UTI) or sexually transmitted disease (STD). Urethritis can also be caused by injury or sensitivity or allergy to chemicals in lotions and other products.
How is urethritis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you and ask about your symptoms and health history. You may also have one or more of the following tests:
Urine test to take samples of urine and have them checked for problems.
Blood test to take a sample of blood and have it checked for problems.
Vaginal culture to take a sample of vaginal discharge to have it tested for problems. A cotton swab is inserted into the vagina.
Cystoscopy to allow the healthcare provider to look for problems in the urinary tract. The test uses a thin, flexible telescope called a cystoscope with a light and camera attached. The scope is inserted into the urethra.
Ultrasound to allow the healthcare provider to see a detailed image of the inside of your pelvis. Ultrasound will not show whether you have urethritis, but it may show other signs of sexually transmitted diseases that can also cause urethritis. Ultrasound will not show whether you have urethritis, but it may show other signs of sexually transmitted diseases that can also cause urethritis.
Nucleic acid test (NAT) to detect the presence of a virus or bacteria. It may be done instead of a culture because it allows for a faster diagnosis.
How is urethritis treated?
Treatment depends on the cause of urethritis. If it’s due to a bacterial infection, antibiotics (medicines that fight infection) will be given. Your healthcare provider can tell you more about your treatment options. In the meantime, your symptoms can be treated. To relieve pain and swelling, anti-inflammatory medicines, such as ibuprofen, may be given. Untreated, symptoms may get worse. It can also cause scar tissue to form in the urethra, causing it to narrow. And, it can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease.
When to call your healthcare provider
Call the healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following:
Fever of 100.4°F (38.0°C) or higher
Burning pain with urination
Abdominal or pelvic pain
Increased urge to urinate
Discharge from the vagina
Preventing STDs
When it comes to sex, it’s important to take care and be safe. Any sexual contact with the penis, vagina, anus, or mouth can spread an STD. The only sure way to prevent STDs is abstinence (not having sex). But there are ways to make sex safer. Use a latex condom each time you have sex. And talk to your partner about STDs before you have sex.
Updated:
March 20, 2017
Reviewed By:
Goode, Paula, RN, BSN, MSN,Greenstein, Marc, DO,Image reviewed by StayWell medical illustration team.