Treating Varicocele
Treating Varicocele
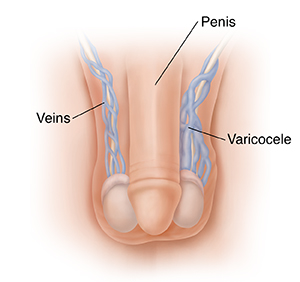
A varicocele is when the veins in your scrotum are enlarged. The scrotum is the pouch of skin that holds your testicles. A varicocele is like the varicose veins found in legs, only it is in the scrotum.
In most cases, a varicocele is not serious. Your healthcare provider may wait and watch the problem for a while. If needed, surgery or another procedure is done to close off the enlarged veins. This may be advised if:
- You have pain
- You don't like how the veins look
- You and your partner are having trouble getting pregnant
Open varicocelectomy surgery
Your healthcare provider may advise surgery to tie off the enlarged veins around the testicles:
-
You are given anesthesia to keep you comfortable. You may or may not be asleep. This will depend on the medicine you are given.
-
A cut is made in the groin or in the lower belly.
-
The veins are then cut and tied off.
-
The cut is closed with stitches, staples, or surgical tape.
Laparoscopic varicocelectomy surgery
Instead of open surgery, laparoscopic surgery may be advised. This is surgery done through a few tiny cuts. It uses a thin tool (laparoscope):
-
You are given general anesthesia. This will make you sleep during the procedure.
-
A few small cuts are made in the lower belly. The laparoscope is put in through 1 cut. Tiny surgical tools are put in through the other small cuts.
-
The laparoscope sends enlarged pictures to a computer screen. Using these pictures, the surgeon finds the veins that need treatment.
-
The veins are clamped to seal them off.
-
The tools are taken out. The cuts are closed with stitches, staples, or surgical tape.
Percutaneous embolization
In place of surgery, your healthcare provider might advise sealing off the enlarged veins. This is done using percutaneous embolization. A radiologic procedure called a venogram is used to make a map of the veins. A tube is then placed in the large vein in the groin. Materials are injected through this tube into the enlarged veins to block them off.
After your varicocele procedure
-
You may feel some pain in your testicle for a few days.
- Mild swelling and bruising is expected.
-
Mild swelling around the testicle is normal after the procedure. Put an ice pack wrapped in a clean, thin towel on the area to help. Do this for no longer than 20 minutes at a time.
-
Plan to rest for 5 to 7 days.
When to call your healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have:
-
Ongoing pain not eased by pain medicine
-
Black-and-blue around the cut, bleeding from the cut, or swelling in the scrotum
-
A fever above 100.4°F (38°C)
-
Greenish or bad-smelling drainage from the cut
Risks of varicocele repair
Risks and possible complications of these procedures include:
-
Blood clot
-
Infection
-
Fluid accumulation around testicle (hydrocele)
-
Injury to the nerves in the groin or scrotum
-
Injury to scrotal tissue or structures
-
Injury to the artery that supplies blood to the testicle
-
Risks of general anesthesia, if used
-
Damage to belly structures (laparoscopic surgery)
Updated:
September 17, 2019
Reviewed By:
Marc Greenstein MD,Marianne Fraser MSN RN,Raymond Kent Turley BSN MSN RN