Respiratory Distress Syndrome in the Premature Infant
Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) in the Premature Infant
RDS is a breathing problem common in premature infants. Many babies born at under 34 to 36 weeks gestational age have some RDS. Your baby may be cared for in the NICU (neonatal intensive care unit) or in another part of the hospital.
What causes RDS?
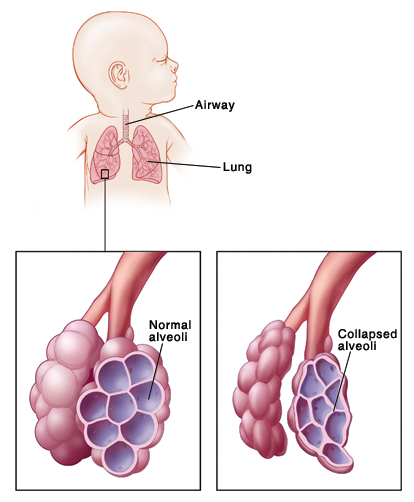
RDS occurs because the lungs have not developed fully enough to produce a substance called surfactant. This substance is needed for normal breathing. When fresh air is breathed in, it travels through airways in the lungs to tiny air sacs (alveoli). Oxygen passes from the air sacs into the bloodstream. Waste air is then breathed out. Normally, surfactant helps keep the alveoli open after exhaling. That way, fresh air can be breathed in easily. But if the lungs contain little or no surfactant, the air sacs collapse after each breath. The baby has to work very hard to reopen them. Babies with RDS may not be strong enough to keep breathing without help.
How is RDS treated?
Treatments depend on how severe and persistent RDS is. They can include:
Artificial surfactant. Each dose is given through an endotracheal tube (ETT). This is a tube that goes through the baby’s mouth or nose into the windpipe. Using this tube, 1 to 4 doses of surfactant may be given several hours apart. If the baby responds well and breathes better without help, the tube may then be removed.
Oxygen without ventilation. This is often given with a nasal cannula (soft tubes fixed under the baby’s nostrils). Or it can be given with an oxygen hood (clear plastic box that fits around the baby’s head). These devices give your baby oxygen without inserting tubes into the baby’s airway.
CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure). A CPAP machine provides continuous air flow into the baby’s airways. This helps keep alveoli from collapsing. CPAP may be used with or without supplemental oxygen.
Ventilator. This machine takes over some or all of the work of breathing. First, an ETT is inserted. The ventilator is then attached and used to send air into the lungs to help the baby breathe. To avoid damage to the lungs, the machine uses the lowest amount of pressure that works to fill the baby's lungs with air. The ventilator is used until the baby’s lungs are making surfactant and the baby is strong enough to breathe without help.
What are the long-term effects?
For many babies, RDS has no long-term effects. Even if alveoli are damaged, the baby is still able to grow new alveoli. If complications do occur they can include:
Increased sensitivity to lung irritants
Increased risk of respiratory infections
Lung damage due to RDS or long-term ventilation, which can sometimes lead to bronchopulmonary dysplasia (persistent breathing difficulties)
Updated:
January 20, 2018
Sources:
Overview of neonatal respiratory distress: disorders of transition. UpToDate.
Reviewed By:
Freeborn, Donna, PhD, CNM, FNP,Lee, Kimberly G., MD, MSc, IBCLC