Pulmonary (Lung) Histoplasmosis
Pulmonary (Lung) Histoplasmosis
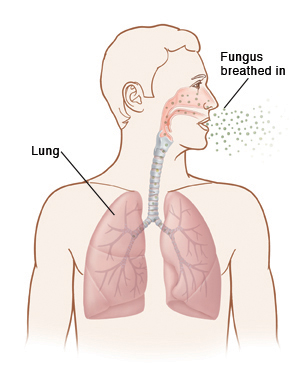
What is pulmonary histoplasmosis?
Pulmonary histoplasmosis is an infection caused by a fungus called Histoplasma capsulatum. Parts of the fungus, called spores, are inhaled into the lungs. This fungus can be found in soil or other material with bird or bat droppings. In the U.S., it is most common in the Mississippi and Ohio River valleys. Those most likely to have serious problems with this disease are:
Infants
Young children
Older adults
Those with long-term lung problems or weak immune systems
What are the symptoms of pulmonary histoplasmosis?
Many people with this lung infection have no symptoms. Often, the diagnosis is first suggested by a chest X-ray done for another purpose. If symptoms do occur, they may include:
Fever
Chills
Dry cough
Chest pain
Joint pain
How is pulmonary histoplasmosis diagnosed?
You may have one or more of these tests:
Blood and urine tests may help diagnose the problem
Sputum cultures check mucus that is coughed up from the lungs for the fungus
Imaging tests, such as chest X-ray, or CT scan, or MRI scans of the lungs
Biopsy checks small samples of lung tissue for the fungus
How is pulmonary histoplasmosis treated?
Many people require no treatment. The infection may go away on its own. You may be prescribed antifungal medicines that are either injected into a vein (intravenous or IV) or taken by mouth (oral). You may need to take the medicines for months. Your healthcare provider can tell you more about your condition, treatment, and what to expect.
Can pulmonary histoplasmosis be prevented?
You can reduce your risk of exposure to this infection. Avoid places with large amounts of bird or bat droppings. If you need to work in these areas, wear a protective breathing mask.
When to call your healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following:
Fever
Chest pain
Coughing up blood
Shortness of breath
Extreme tiredness
Loss of appetite and weight loss
Symptoms that don’t get better with treatment
Updated:
March 21, 2017
Reviewed By:
Blaivas, Allen, J., DO,Image reviewed by StayWell medical illustration team.,Sather, Rita, RN