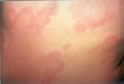
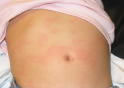
Hives
Hives
Does this describe your symptoms? |
Click image for more info |
Definition
General
Causes of Hives
Definitions
|
If not, see these topics
|
When to Call Your Doctor |
Call 911 Now (you may need an ambulance) If |
|
|
|
Call Your Doctor Now (night or day) If |
|
|
|
Call Your Doctor Within 24 Hours (between 9 am and 4 pm) If |
|
|
|
Call Your Doctor During Weekday Office Hours If |
|
|
|
Self Care at Home If |
|
|
HOME CARE ADVICE FOR HIVES |
Hives from Food Reaction
Food Related Hives:
Foods can cause transient hives, especially around the mouth.
Some are mild food allergies; others can occur in anyone (e.g., with strawberries).
Hives from foods usually disappear within 6 hours.
Antihistamine (e.g., Benadryl) for Hives from Food:
One or two dosages of an antihistamine will accelerate the clearing of this type of hives.
Benadryl (diphenhydramine) is an antihistamine. The adult dose is 25-50 mg. If the hives are still present after 6 hours, repeat the Benadryl.
If Benadryl is not available, use any hay fever or cold medicine that contains an antihistamine. Examples of other antihistamines are chlorpheniramine (Chlortrimeton, Chlor-tripolon) and loratadine (Claritin, Alavert). Loratadine is a newer (second generation) antihistamine and it causes less sedation than diphenhydramine.
CAUTION: This type of medication may cause sleepiness. Do not drink alcohol, drive or operate dangerous machinery while taking antihistamines. Do not take these medications if you have prostate enlargement.
Read the package instructions thoroughly on all medications that you take.
Prevention: In the future, avoid any food you think caused the hives.
Call Your Doctor If:
Severe hives or severe itching persist more than 24 hours despite taking an antihistamine (e.g., Benadryl).
You become worse.
Localized Hives
Localized Hives:
For localized hives, wash the allergic substance off the skin with soap and water.
If itchy, massage the area with a cold washcloth or ice.
Localized hives usually disappear in a few hours and don't need treatment with an oral antihistamine (e.g., Benadryl).
Hydrocortisone Cream:
For very itchy spots, apply hydrocortisone cream 4 times a day as needed.
It is available over-the-counter in U.S. as 0.5% and 1% cream.
Available over-the-counter in Canada as 0.5% cream.
Prevention: Try to avoid any substance that you think caused the hives.
Call Your Doctor If:
Severe hives or severe itching persist more than 24 hours despite taking an antihistamine (e.g., Benadryl).
Hives last more than 1 week.
You become worse.
Widespread Hives
Widespread Hives:
Remove allergens. For widespread hives be certain to take a bath or shower, if triggered by pollens or animal contact. Change clothes.
Take a cool bath for 10 minutes to relieve itching. Rub very itchy areas with an ice cube for 10 minutes.
Hives normally come and go for 3 or 4 days, then disappear.
Antihistamine (e.g., Claritin) for Widespread Hives:
Take an antihistamine like loratadine (e.g., OTC Claritin, Alavert) for widespread hives that itch. The adult dosage of loratadine is 10 mg by mouth once each day. Continue the antihistamine until the hives have been gone for 24 hours.
Loratidine is a newer (second generation) antihistamine and it causes less sedation than diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or Chlorpheniramine (Chlortrimeton).
CAUTION: This type of medication may cause sleepiness. Do not drink alcohol, drive or operate dangerous machinery while taking antihistamines. Do not take these medications if you have prostate enlargement.
Read the package instructions thoroughly on all medications that you take.
Contagiousness: Hives are not contagious. You can return to work or school if the hives do not interfere with normal activities.
Prevention: If you identify a substance that causes hives, try to avoid that substance in the future.
Call Your Doctor If:
Severe itching persists more than 24 hours while taking an antihistamine
Hives persist more than 1 week
You become worse.
And remember, contact your doctor if you develop any of the "Call Your Doctor" symptoms.
Updated:
March 22, 2017