Atelectasis
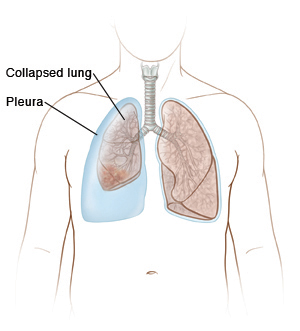
Atelectasis
Atelectasis is the collapse of one or more sections, or lobes, of the lungs. When you breathe in, the lungs normally expand to fill with air. With atelectasis, a blockage in or pressure in the area around the lung (pleura) keeps the lung from expanding.
What causes atelectasis?
Atelectasis is caused by a blocked airway, or from pressure from outside the lung. Some causes include:
An object or tumor in an airway
Mucus blocking an airway
Certain lung diseases, including infections
Fluid or air buildup in the space around the lung (pleura)
What are the symptoms of atelectasis?
The symptoms include:
Difficulty breathing
Pain in the chest
How is atelectasis diagnosed?
You may have one or more of the following tests:
Lab tests to check the level of oxygen and other gases in the blood.
Chest X-rays create images of the lungs.
CT scans create detailed pictures of the lungs.
Bronchoscopy allows the healthcare provider to see inside the airways using a bronchoscope.
How is atelectasis treated?
Treating the underlying cause often allows the lung to re-expand. Pneumonia (a serious lung infection) often occurs when the lung collapses. In order to help the lung tissue re-expand and prevent pneumonia, the following treatments may be prescribed:
Chest percussion to loosen mucus and help prevent pneumonia. It involves clapping on the chest with a cupped hand.
Postural drainage to help drain mucus from the lungs. It requires lying in certain positions for a given amount of time.
Deep breathing exercises to help expand the lungs and clear mucus. They also help prevent pneumonia.
Incentive spirometry to encourage deep breathing
Inhaled medicines to open up the airway. If infection is present, antibiotics may also be given.
Bronchoscopy to remove secretions or foreign objects that may be causing the blockage.
When to call the healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider, or 911 for severe symptoms, if you have any of these:
A bluish color to the skin
Fever of 100.4° (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your healthcare provider
Continued cough
Wheezing or fast breathing
Tiredness
Updated:
October 03, 2017
Sources:
Flexible Bronchoscopy: Indications and Contraindications. UpToDate.
Reviewed By:
Blaivas, Allen J., DO,Sather, Rita, RN