Anemia
Anemia
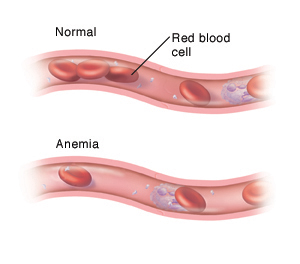
Anemia is a condition that occurs when your body does not have enough healthy red blood cells (RBCs). RBCs are the parts of your blood that carry oxygen throughout your body. A protein called hemoglobin allows your RBCs to absorb and release oxygen. Without enough RBCs or hemoglobin, your body doesn't get enough oxygen. Symptoms of anemia may then occur.
What are the symptoms of anemia?
Some people with anemia have no symptoms. But most people have symptoms that range from mild to severe. These can include:
Tiredness (fatigue)
Weakness
Pale skin
Shortness of breath
Dizziness or fainting
Rapid heartbeat
Trouble doing normal amounts of activity
Jaundice (yellowing of your eyes, skin, or mouth; dark urine)
What causes anemia?
Anemia can occur when your body:
Loses too much blood
Does not make enough RBCs
Destroys your RBCs at a faster rate than it can replace them
Does not make a normal amount of hemoglobin in your RBCs
These problems can occur for many reasons, including:
A condition that you are born with (congenital or inherited), such as sickle cell disease or thalassemia
Heavy bleeding for any reason, including injury, surgery, childbirth, or even heavy menstrual periods
Being low in certain nutrients, such as iron, folate, or vitamin B12, possibly from a poor diet or a condition like celiac disease or Crohn's disease
Certain chronic conditions like diabetes, arthritis, or kidney disease
Certain chronic infections like tuberculosis or HIV
Exposure to certain medicines, such as those used for chemotherapy
There are different types of anemia. Your healthcare provider can tell you more about the type of anemia you have and what may have caused it.
How is anemia diagnosed?
To diagnose anemia, your healthcare provider orders blood tests. These can include:
Complete blood cell count (CBC). This test measures the amounts of the different types of blood cells.
Blood smear. This test checks the size and shape of your blood cells. To do the test, a drop of your blood is viewed under a microscope. A stain is used to make the blood cells easier to see.
Iron studies. These tests measure the amount of iron in your blood. Your body needs iron to make hemoglobin in your RBCs.
Vitamin B12 and folate studies. These tests check for some of the components that help give RBCs a normal size and shape.
Reticulocyte count. This test measures the amount of new RBCs that your bone marrow makes.
Hemoglobin electrophoresis. This test checks for problems with your hemoglobin in RBCs.
How is anemia treated?
Treatment for anemia is based on the type of anemia, its cause, and the severity of your symptoms. Treatments may include:
Diet changes. This involves increasing the amount of certain nutrients in your diet, such as iron, vitamin B12, or folate. Your healthcare provider may also prescribe nutrient supplements.
Medicines. Certain medicines treat the cause of your anemia. Others help build new RBCs or relieve symptoms. If a medicine is the cause of your anemia, you may need to stop or change it.
Blood transfusions. Replacing some of your blood can increase the number of healthy RBCs in your body.
Surgery. In some cases, your doctor may do surgery to treat the underlying cause of anemia. If you need surgery, your healthcare provider will explain the procedure and outline the risks and benefits for you.
What are the long-term concerns?
If you have a certain type of anemia, you can expect a full recovery after treatment. If you have other types of anemia (especially a type you're born with), you will need to manage it for life. Your doctor can tell you more.
Updated:
March 20, 2017
Sources:
Approach to the adult patient with anemia. UpToDate.
Reviewed By:
Freeborn, Donna, PhD, CNM, FNP,Gersten, Todd, MD,Image reviewed by StayWell medical illustration team.