Bariatric Surgery: Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Bariatric Surgery: Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
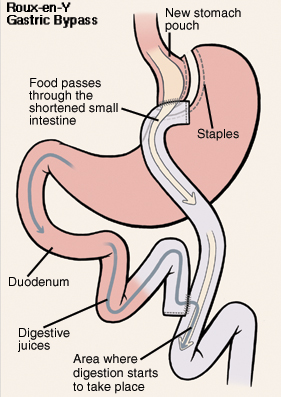
Bariatric surgery changes the size of your stomach and the length of your small intestine that comes in contact with the food you eat. The goal is to limit how much food can be eaten and/or absorbed at one time. Bariatric surgery can be done in several ways. You are having a Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB). This is the most common type of bariatric surgery. During this type of procedure, part of the stomach is separated from the rest of the stomach and closed off with staples to create a smaller pouch. The smaller stomach helps restrict the amount of food you can eat at one time. The small intestine is then divided, and part of it is reattached to the stomach pouch. Because some of the small intestine is bypassed, less food is absorbed as well.
The procedure
A large portion of the stomach is closed off. This leaves a small pouch to hold food, restricting the amount that can be eaten at one time. The small intestine is cut below the duodenum and reattached to the new stomach pouch. This leaves a shortened path for food to travel through. As a result, some of the food that is eaten is expelled as waste and not absorbed as energy. The remaining pouch of the stomach and duodenum are also reattached to the small intestine farther down to drain stomach, biliary and pancreatic enzymes, and fluids.
Bariatric surgery is designed to cause a large amount of weight loss. Rapid weight loss can cause deposits in the gallbladder called gallstones. The gallbladder may need to be removed at a later date. If you already have gallstones, the gallbladder may be removed at the time of your RYGB operation.
All types of bariatric surgery have different advantages and disadvantages. Be sure to discuss the risks and complications of this surgery, and any alternatives with your healthcare provider.
Updated:
March 16, 2019
Sources:
Bariatric surgical operations for the management of severe obesity: Descriptions. UpToDate
Reviewed By:
Raymond Kent Turley BSN MSN RN