Peritoneal Dialysis (PD)
Peritoneal Dialysis (PD)
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a way to cleanse the blood to treat kidney failure. It uses the lining of your abdomen called the peritoneal membrane and a special solution (dialysate). The solution needs to be changed several times a day. This can be done as part of your home or work routine. Or it can be done at night by a machine. Dialysate is put inside your belly (abdomen) through a plastic tube (catheter). This catheter is surgically placed into your abdomen. It takes the catheter site 2 to 4 weeks to heal before you can use it. Your doctor may tell you to have this catheter put in place before your kidneys fail completely.
How PD works
The abdomen is filled with dialysate through the catheter and allowed to remain (dwell) for 4 to 6 hours. The membrane and dialysate then work to clean the blood. The dialysate needs to be changed every few hours. This is called an exchange.
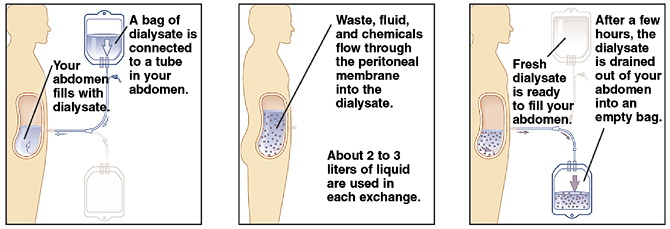
Your experience
-
You can do PD at home, work, or where ever is convenient.
-
A nurse or technician will teach you how to do PD exchanges and care for the PD tube.
-
You have an increased risk of infection in your abdomen (peritonitis). It is very important to carefully follow all instructions to prevent infection.
-
You will need to weigh yourself every day to make sure you don't have too much fluid in your body.
-
You will need to follow a special diet.
There are 2 ways to do exchanges:
-
Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). With this, you do your own exchanges 3 to 5 times per day , each with a dwell time of about 4 to 6 hours (you can have a longer dwell time overnight). Each exchange takes about 30 to 40 minutes each.
-
Cyclic peritoneal dialysis (CCPD). This uses a machine called a cycler. The cycler does most of your exchanges at night while you sleep. You have a long dwell time during the day. You may also do manual daytime exchanges, which take 30 to 40 minutes each.
When to call your healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following:
-
Fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your healthcare provider
-
Chills
-
Dialysate that is cloudy or bloody when it drains from your body
-
Pain in your abdomen or around your catheter
-
Skin around your catheter is warm, red, or has drainage
-
Blocked flow into or out of your catheter
-
Part of your belly appears to be bulging out (hernia)
Updated:
March 16, 2019
Reviewed By:
Walead Latif MD