Deciding on Bariatric Surgery
Deciding on Bariatric Surgery
Is excess weight affecting your life and your health? Bariatric surgery (also called obesity surgery) may help you reach a healthier weight. This surgery alters your digestive system. For the surgery to work, you must change your diet and lifestyle. In most cases, the surgery is not reversible. So if you’re considering surgery, learn all you can about it before you decide. Bariatric surgery also has a number of potential risks and complications that you need to discuss with your surgeon.
Qualifying for surgery
Surgery is not for everyone. To qualify:
-
You must have a BMI of 40 or more, or a BMI of 35 or more (see box below) plus a serious obesity-related health problem, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea.
-
You must be healthy enough to have surgery.
-
You may be required to have a psychological evaluation.
-
You must have tried to lose weight by other means, such as diet and exercise.
Setting realistic expectations
The goal of bariatric surgery is to help you lose over half of your excess weight. This can improve or prevent health problems. This surgery is not done for cosmetic reasons. Keep in mind that:
-
Other weight-loss methods should be tried first. Lifestyle changes, behavioral modifications, and prescription medicines are initial choices. Surgery is only a choice if other methods don’t work.
-
Surgery is meant to be permanent. You will need to change how you eat for the rest of your life.
-
You must commit to eating less and being more active after surgery. If you don’t, you will not lose or keep off the weight.
-
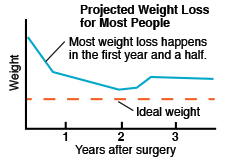
You won’t reach a healthy weight right away. Most weight is lost steadily during the first year or two after surgery.
-
Most likely, you won’t lose all your excess weight. But you can reach a much healthier weight, and maintain it by following your doctor's advice for diet and exercise.
Obesity is measured by a formula called body mass index (BMI), which is based on your height and weight. A healthy BMI is about 18 to 25. A BMI of 30 or more signals obesity. A BMI of 35 or more is severe obesity. A BMI of 40 or more reflects morbid obesity.
Resources
-
American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery
www.asmbs.org
-
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Obesity Education Initiative
www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/public/heart/obesity/lose_wt
Updated:
January 17, 2020
Sources:
Bariatric operations for management of obesity: Indications and preoperative preparation, Up To Date
Reviewed By:
Fetterman, Anne, RN, BSN