Bee Sting
Bee Sting
Does this describe your symptoms? |
Click image for more info |
Definition
General Information
Sting Symptoms
Removing the Stinger
Anaphylaxis
Preventing Stings - Some Outdoor Activity Tips
|
If not, see these topics
First Aid:FIRST AID Advice for Minor Bee Sting (localized symptoms only):
FIRST AID Advice for Anaphylaxis - Epinephrine (pending EMS arrival):
Epinephrine is available in autoinjectors under trade names: Epi-Pen, Epi-Pen Jr, and Twinject. Epi-Pen is a single injection. Twinject has a second injection that can be used if there is no improvement after 5 minutes. FIRST AID advice for ANAPHYLAXIS - BENADRYL (pending EMS arrival):
FIRST AID ADVICE for Anaphylactic Shock (pending EMS arrival):
|
When to Call Your Doctor |
Call 911 Now (you may need an ambulance) If |
|
|
|
Call Your Doctor Now (night or day) If |
|
|
|
Call Your Doctor Within 24 Hours (between 9 am and 4 pm) If |
|
|
|
Call Your Doctor During Weekday Office Hours If |
|
|
|
Self Care at Home If |
|
|
HOME CARE ADVICE |
Care Advice for Bee - Wasp - Yellow Jacket Sting
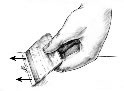
Try to Remove the Stinger (if present):
The stinger looks like a tiny black dot in the sting.
There are several different methods of removal. Removing the stinger quickly is more important than how you remove it.
Use a fingernail, credit card edge or knife-edge to scrape it off. Don't pull it out. (Reason: squeezes out more venom). If the stinger is below the skin surface, leave it alone. It will be shed with normal skin healing.
In many cases no stinger will be present. Only bees leave their stingers. Wasps, yellow jackets, and hornets do not.
Local Cold for Pain - Cold Pack Method:
Wrap a bag of ice in a towel (or use a bag of frozen vegetables such as peas).
Apply this cold pack to the area of the sting for 10-20 minutes.
You may repeat this as needed, to relieve symptoms of pain and swelling.
Pain Medicines:
For pain relief, take acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or naproxen.
Acetaminophen (e.g., Tylenol):
Take 650 mg by mouth every 4-6 hours. Each Regular Strength Tylenol pill has 325 mg of acetaminophen.
Another choice is to take 1,000 mg every 8 hours. Each Extra Strength Tylenol pill has 500 mg of acetaminophen.
The most you should take each day is 3,000 mg.
Ibuprofen (e.g., Motrin, Advil):
Take 400 mg by mouth every 6 hours.
Another choice is to take 600 mg by mouth every 8 hours.
Use the lowest amount that makes your pain feel better.
Naproxen (e.g., Aleve):
Take 250-500 mg by mouth every 12 hours.
Use the lowest amount that makes your pain feel better.
Extra Notes:
Acetaminophen is thought to be safer than ibuprofen or naproxen in people over 65 years old. Acetaminophen is in many OTC and prescription medicines. It might be in more than one medicine that you are taking. You need to be careful and not take an overdose. An acetaminophen overdose can hurt the liver.
Caution: Do not take acetaminophen if you have liver disease.
Caution: Do not take ibuprofen or naproxen if you have stomach problems, kidney disease, are pregnant, or have been told by your doctor to avoid this type of medicine. Do not take ibuprofen or naproxen for more than 7 days without consulting your doctor.
Before taking any medicine, read all the instructions on the package
Hydrocortisone Cream for Itching:
Hydrocortisone cream applied to the sting area 4 times a day can also help reduce itching. Use it for a couple days, until the itch is mild.
Available over-the-counter in U.S. as 0.5% and 1% cream.
Available over-the-counter in Canada as 0.5% cream.
Antihistamine Medication for Itching: If the sting becomes very itchy, take diphenhydramine (e.g., Benadryl; adult dosage 25-50 mg) by mouth.
Do not take diphenhydramine if you have prostate problems.
Antihistamines may cause sleepiness. Do not drink, drive, or operate dangerous machinery while taking antihistamines.
Read the package instructions thoroughly on all medications that you take.
Expected Course:
Pain: Severe pain or burning at the site lasts 1 to 2 hours. Pain after this period is usually minimal. Itching often follows the pain.
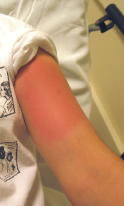
Redness and Swelling: Normal redness and swelling from the venom can increase for 24 hours following the sting. Redness at the sting site is normal. It doesn't mean that it is infected. The redness can last 3 days and the swelling 7 days.
Stings only rarely get infected.
Call Your Doctor If:
Difficulty breathing or swallowing (generally develops within the first 2 hours after the sting; call 911)
Swelling becomes huge
Sting begins to look infected
You become worse
Preventing Stings Because they Hurt A Lot
Some Outdoor Activity Tips
Wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and shoes when you are in grassy areas or outdoors and exposed to stinging insects.
Avoid using perfumes and hair sprays; these attract insects.
Wear dark or drab colored clothes rather than bright colors.
Take special care when eating or preparing food outdoors. These odors can attract insects (especially yellow jackets).
Tetanus Vaccination and Stings
Getting a Tetanus Booster:
Tetanus vaccination (booster) after a bee sting is not necessary.
However, if it has been more than 10 years since your last tetanus vaccination, it is appropriate from a preventive health care standpoint to obtain a vaccination (i.e., Td or TDaP) sometime in the next couple weeks.
And remember, contact your doctor if you develop any of the "Call Your Doctor" symptoms.
Updated:
March 22, 2017