Peritonsillar Abscess
Peritonsillar Abscess
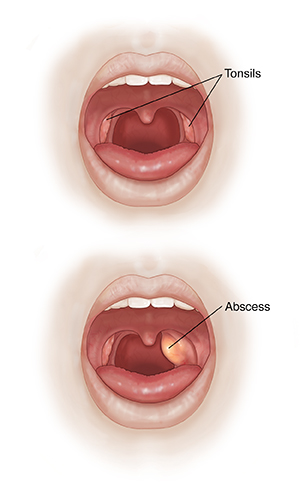
Signs and symptoms of peritonsillar abscess
Severe sore throat (often worse on one side)
Swollen and enlarged tonsils
Fever and chills
Pain when swallowing or trouble opening the mouth
Voice changes
Drooling
Swollen or tender glands in the neck
Diagnosing peritonsillar abscess
Your healthcare provider will examine you and look inside your mouth and throat. You will be asked about your symptoms and health history. Tests or procedures may be done as well, including those listed below.
Throat swab. This test checks for infection. It is done by wiping a sterile cotton swab in the back of the throat. The swab is then sent to a lab for study.
Blood tests. These might be done to check how your body is responding to the infection.
Ultrasound or computed tomography (CT) scans. These tests provide images of the abscess. They also help rule out other problems.
Needle aspiration. This procedure removes a sample of pus from the abscess with a needle. The sample is then sent to a lab to check for infection. In some cases, all of the pus is removed from the abscess.
Treating peritonsillar abscess
The abscess itself can be treated. Treatment of the underlying infection is also needed. Common treatments are listed below.
Medicines. Antibiotics are needed to treat the underlying infection. These may be taken by mouth or given by IV. Pain relievers may also be given, if needed.
Drainage of the abscess. A procedure may be needed to drain the pus from the abscess. Pus may be removed from the abscess with a needle (needle aspiration). Or, a small incision is made in the abscess. The pus is then drained and suctioned from the throat and mouth. This is called incision and drainage.
Tonsillectomy. This is surgery to remove the tonsils. It may be done if the abscess does not improve with medicines. It may also be done if you have frequent tonsil infections or abscesses.
Recovery and follow-up
Treating the bacterial infection generally relieves the problem. Once the infection resolves, you should recover completely. Follow up with your healthcare provider as directed. And if you develop another throat infection, see your healthcare provider promptly.
Updated:
June 14, 2018
Sources:
Costantino, T. MD "Randomized Trial Comparing Intraoral Ultrasound to Landmark-based Needle Aspiration..." AEM (2012) 19:6 pp. 626-631
Reviewed By:
Fraser, Marianne, MSN, RN,Image reviewed by StayWell medical illustration team.,Kacker, Ashutosh, MD